Preventing Diabetic Vision Loss
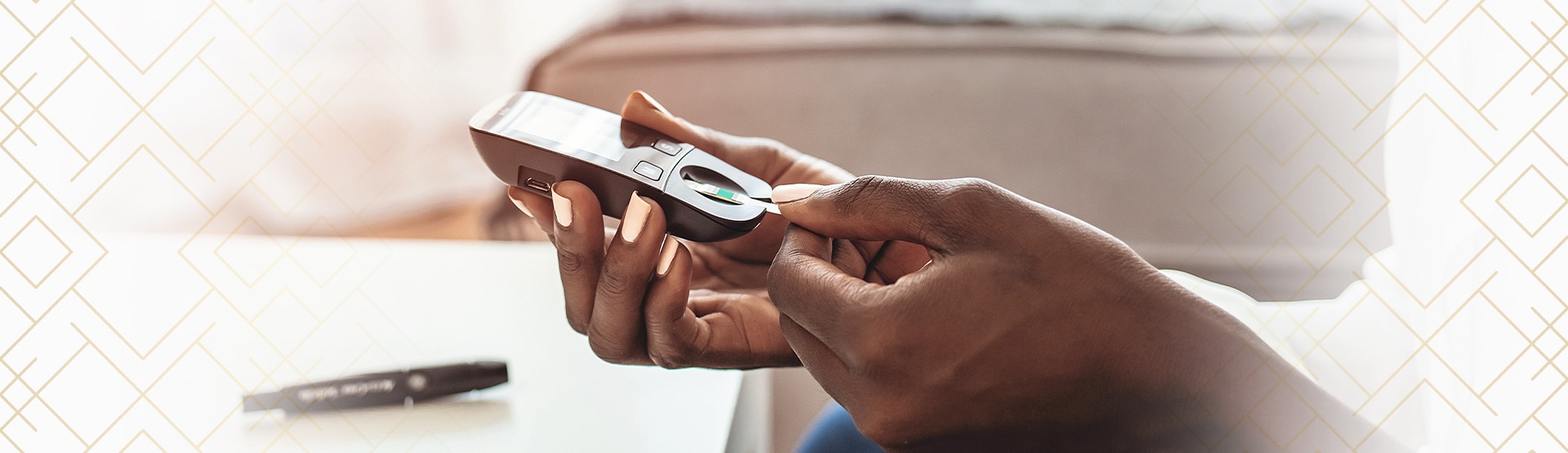
Diabetes is a disease affecting how the body uses or produces insulin, a hormone that controls blood glucose (sugar) levels.
Those with diabetes have a higher risk of developing various health conditions, including eye problems. The longer you have diabetes, the more likely you are to develop diabetic eye disease.
Diabetic eye exams are comprehensive exams focused on eye health and vision issues affected by diabetes. Annual diabetic eye exams can help monitor your eyes for changes, manage your symptoms, and prevent vision loss.

How Diabetes Affects Sight
Our bodies use blood glucose as energy. Those with diabetes are unable to effectively use blood glucose, resulting in rising blood glucose levels and weakened cells. Blood cells can weaken and leak, including the blood vessels inside the eye.Abnormal blood vessels can grow under the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The weakened, leaky blood vessels can block blood flow and increase fluid inside the eye, leading to increased intraocular pressure (IOP). As a result, various eye functions can be affected, decreasing vision. Damaged eye tissue can also lead to permanent vision loss.

What Is Diabetic Eye Disease?
When diabetes is uncontrolled, it can contribute to changes in eye tissue and eye health. Diabetes can cause changes to your eye muscles, worsen nearsightedness and farsightedness, and even lead to premature presbyopia. Over time, these changes can lead to diabetic eye disease.
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common form of diabetic eye disease. It can also lead to diabetic macular edema, glaucoma, and early cataract development.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when the blood vessels nourishing the retina (the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye) weaken or swell, resulting in blood and fluid leakage. There are 2 forms of diabetic retinopathy:
- Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, the earliest stage, occurs when blood vessels weaken. At this stage, you can experience visual symptoms, but the condition is usually not (yet) sight-threatening.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy, the advanced stage, occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow, decreasing blood circulation and depriving the retina of oxygen. At this stage, you can experience vision changes and an increased risk of vision loss and retinal detachment.
When retinopathy progresses, it can lead to blindness, so if you have this condition, your eye health will be closely monitored through diabetic eye exams until you need treatment. Signs and symptoms of retinopathy may include:
- Black or empty spots in your vision
- Blurry vision
- Inability to see colours
- Loss of central vision
- Peripheral flashes of light
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy can include anti-VEGF injections, laser therapy, or a vitrectomy (replaces the vitreous). Early detection is crucial, as treatment is more likely to be successful when it’s started early.
Diabetic Macular Edema
Diabetic macular edema is a complication of diabetic retinopathy caused by excess fluid in the eye. When leaky blood vessels under the retina release fluid, it causes the macula to thicken and swell.
The macula is an oval-shaped tissue at the retina’s centre. It helps us see straight ahead, colour, and fine details. A compromised macula can decrease your central and colour vision and cause symptoms like wavy lines or faded colours.
Diabetic macular edema cannot be cured but can be slowed, and your symptoms improved with treatment. There are surgical and nonsurgical approaches to managing this condition.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of blindness in Canada. The disease affects the optic nerve, which is responsible for delivering visual information from the retina to the brain. Optic nerve damage leads to vision loss.
Those with diabetes have a higher risk of developing glaucoma. High blood sugar levels weaken blood vessels, leading to fluid leaking into the eye. The excess fluid builds eye pressure, slowly deteriorating the optic nerve. Measuring increased eye pressure is a standard part of diabetic eye exams and is usually included in a complete eye exam.
Early detection is crucial for preventing glaucoma, or managing it before more vision is lost. Reducing eye pressure with eye drops or medications is often the first step. However, more severe symptoms may be treated with laser surgery or a combination of treatments.
Cataracts
The eye’s normally clear lens can become cloudy and opaque when proteins break down, causing clumps called cataracts. The cloudy areas can begin small or grow large, affecting vision more severely over time. Many people develop cataracts when they’re over 60, as lens proteins naturally change with aging. But those with diabetes can develop cataracts earlier.
High sugar levels in the aqueous humour (the fluid that supplies the lens with nutrients and oxygen) can cause the lens to swell, resulting in blurry vision. Enzymes in the lens can also interact with the sugar, changing the lens’ makeup, and breaking down proteins.
Minor cataracts may not impact your vision or can be improved with glasses or contact lenses. But larger, more opaque cataracts can impair your sight at all distances. When cataracts significantly impact lens function, the lens can be surgically removed.
Cataract surgery removes the impaired lens and replaces it with an artificial lens. Eye Q Optometry offers cataract surgery co-management to guide you through the process from start to finish and the years to come.
Visit Us for Diabetic Eye Health
Diabetic eye exams are essential for those with diabetes by monitoring warning signs and early symptoms of diabetic eye disease. We can help prevent vision loss and manage your symptoms.
For more information about how diabetes can affect your sight, contact us.
Visit Us Today
Our practice is located in the Killarney area of 17th Avenue, within walking distance of the Westbrook LRT station. There’s plenty of parking available nearby.

Our Address
- 3314 17 Ave SW
- Calgary, AB T3E 0B4
Contact Information
- Phone: 403.727.4404
- Fax: 888.457.6613
- Email: [email protected]
Our Hours
- Monday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
- Tuesday: 11:00 AM – 7:00 PM
- Wednesday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
- Thursday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
- Friday: 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM
- Saturday: 10:00 AM – 4:00 PM
- Sunday: Closed